Syllabus Sections
- 1.2 Operations With Rational Numbersmr. Mac's Page Key
- 1.2 Operations With Rational Numbersmr. Mac's Page Number
- 1.2 Operations With Rational Numbersmr. Mac's Page Numbers
Publish Date
08/15/2012 23:36:42
Basic Math Skills
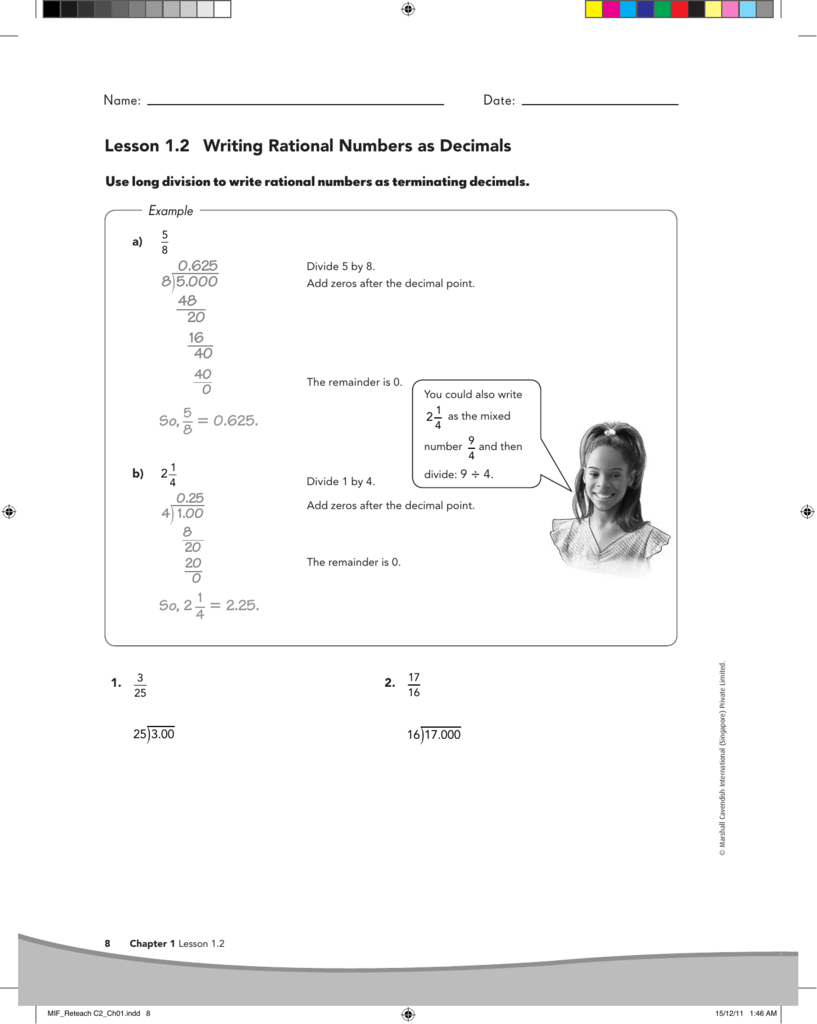
IBM Software systems and applications are designed to solve the most challenging needs of organizations large and small, across all industries, worldwide. Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide rational numbers. Convert a rational number to a decimal using long division; know that the decimal form of a rational number terminates in 0’s or eventually repeats. Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the four operations with rational numbers. MAC 1105 is a college level algebra course. This course introduces the student to the concept of functions and their graphs. Students will learn to graph linear, quadratic, rational, exponential, logarithmic, radical, power, and absolute value functions and transformations; perform operations with mathematical expressions and compositions of functions; find the inverse of a function; apply the. Order of Operations Bingo Level 1 includes strategies for reviewing order of operations, a practice worksheet, and a ready-to-use Bingo game. The game can be played with the class, in math centers, in cooperative learning teams, or in small guided math groups. The math game includes 32 unique number. I'm taking MHF4U (Advanced Functions) in Ontario. Is your grade 12 math help the right course for me? Our grade 12 math help also covers topics for classes including: Ontario – Foundations for College Mathematics (MAP4C), & Mathematics for Work and Everyday Life (MEL4E); B.C. – Pre-calculus 12 & Foundations of Mathematics 12; and Alberta – Math 30-1 & Math 30-2.
MATD-0330
Fall 2012
09/24/2012 - 12/16/2012
Course Information
Section 082
Lecture
MWF 10:10 - 11:20
SAC1 1311
Abel Villarreal
Section 134
Lecture
TTh 15:00 - 17:25
SAC1 1320
Abel Villarreal
Office Hours
- M W F
11:20 - 12:00 noon
South Austin Campus (SAC) - M W
1:20 pm - 2:00 pm
South Austin Campus (SAC) - T Th
1:20 - 2:00 pm
South Austin Campus (SAC)
Course Requirements
Course Description and Rationale:
This course is designed to develop and solidify basic arithmetic and algebra skills that will be required in future math courses. The course content includes operations on whole numbers, integers, fractions, decimals, ratios and proportions, and percents. It also includes exploring and solving one-variable linear equations and applications as well as simple algebraic concepts with geometric extensions.
The Basic Math Skills course is designed to be the first of a three-course developmental course sequence that prepares students for college algebra and beyond. The sequence consists of Basic Math Skills (#0330), Elementary algebra (#0370), and Intermediate Algebra (#0390)
Required Text:
Prealgebra, 5th Edition by Blair, Tobey, Slater; ISBN #9781256748649 or 1256748641. This text is the ACC custom edition, which saves money. Used versions are NOT available as this a new edition.
The previous text, Basic Math Skills, 4th Edition contains almost the exact material but do not match on certain page numbers and homework problems. Used copies may be hard to come by.
Free Supplemental Resources:
www.interactmath.com – A web-based resource that offers unlimited online, text-specific tutorial exercises. MacIntosh computers are currently NOT supported.
www.purplemath.com – A web-based resource that offers unlimited practice and alternate explanations on many arithmetic and algebraic topics. Click on “Lesson index” at right to locate specific topics. The home page also has links to more than 15 alternate sites for free tutorials, practice, lessons, etc. as well as assorted math study skills help. This site supports both Mac and PC formats. Very easy to use.
www.austincc.edu/tutor – ACC main campus Learning Labs which offer free tutoring on a first–come first–serve basis. Access site for hours of operation.
http://patrickjmt.com/ – A vast library of short videos on hundreds of math topics. If you want a 3 to 5 minute movie tutorial on any math topic, this is the go-to site. MAC and PC friendly.
Course Grade:
The course grade is determined as follows:
Best 4 of 5 tests + final exam) divided by 5 + homwork average (up to 4 points)
All tests will be administered and monitored on a scheduled class meeting in class. The use of the testing center will be considered only under extreme and unexpected circumstances (power failure, severe weather, etc.) See course timetable.
Homework and Explorations:
There are four (4) homework sets, each based on a 4-point scale. Homework Set 1 covers Chapters 1 and 2. Homework Set 2 covers Chapters 3 and 4, and so on. The homework average (up to 4 points) is then added to the final average. The more homework turned in the more extra credit points earned. Since homework is extra
credit, no more than one (1) homework set will be accepted late.
A related real world exploration will be given between tests and due on each test day. Each exploration will be worth up to 10 bonus test points on each test. There is no penalty for not completing this extra credit. Each exploration is an opportunity to
realistically apply what you learn.
Class Participation:
Doing mathematics in front of your peers solidifys one’s mathematics foundation. I highly recommend that you DO mathematics this way as often as possible. I will keep count on the number of times you contribute to the class discussion and will use this “participation” grade in cases where your average is between an A and B, B and C, etc.
Late Work:
Late work is defined as assigned work that is no more than two (2) class days late. There is a one (1) point penalty for late work. Thus, the highest score a homework set may receive is a 3 out of 4 points. NO MORE than 1 homework set will be accepted and counted late.
In-Progress Grade:
An in-progress (IP) grade is a neutral, non-passing grade. It is not counted in the gpa, but may count as a “withdrawal (W)” for financial aid purposes. It is usually awarded to students who attend class regularly, do all the assigned work and cannot maintain a passing average. The math department chairperson must approved an IP. The student will have to retake the course the next semester AND pay for the course AGAIN. Students may not receive more than two (2) IP’s in this or ANY developmental course.
Makeup Tests:
A student can miss one (1) of the first four tests. NO MORE. Test 5 is optional and may replace a missed test or the lowest of your first 4 test scores. Test 5 cannot be used to replace the final exam.
Attendance Policy:
According to the Texas Success Initiative (TSI), attendance is required in this course. Students with four (4) or more absences MAY BE withdrawn. See an ACC advisor for further clarification.
Readings
Fall 2012 Timetable (16 weeks)
WEEK MONDAY WEDNESDAY FRIDAY
1 Aug. 27 1.1, 1.2 Aug. 29 1.3, 1.4 Aug. 31 1.5, 1.6
2 Sept. 3 Labor Day Sept. 5 1.7, 1.8 Sept. 7 1.9, 2.1
3 Sept. 10 2.2, 2.3 Sept. 12 2.4, 2.5 Sept. 14 2.6
4 Sept. 17 Test #1 Sept. 19 3.1, 3.2 Sept 21 3.3, 3.4
5 Sept. 24 4.1, 4.2 Sept. 26 4.3, 4.4 Sept. 28 4.5, 4.6
6 Oct. 1 Test #2 Oct. 3 5.1, 5.2 Oct. 5 5.3
7 Oct. 8 5.4 Oct. 10 5.5 Oct. 12 5.6
8 Oct. 15 5.7 Oct. 17 Test #3 Oct. 19 6.1, 6.2
9 Oct. 22 6.3 Oct. 24 7.1 Oct. 26 7.2
10 Oct. 29 7.3 Oct. 31 7.4 Nov. 2 7.5
11 Nov. 5 8.1 Nov. 7 8.2 Nov. 9 8.3
12 Nov. 12 8.4 Nov. 14 Test #4 Nov. 16 8.5
13 Nov. 19 8.6 Nov. 21 8.7 Nov. 23 Gobble-Gobble
14 Nov. 26 8.9 Nov. 28 9.1, 9.2 Nov. 30 10.1
15 Dec. 3 10.3,10.5 Dec. 5 10.6 Dec. 7 10.7
16 Dec. 10 Test #5* Dec. 12 Final Review Dec. 14 Final Exam
*(optional)
12 week Timetable
WEEK TUESDAY THURSDAY
1 Sept. 25 1.1 – 1.4 Sept. 27 1.5 – 1.7
2 Oct. 2 1.8, 1.9, 2.1, 2.2 Oct. 4 2.3 – 2.6
3 Oct. 9 Test #1 Oct. 11 3.1 – 3.4
4 Oct. 16 4.1-4.3 Oct. 18 4.4 – 4.6
5 Oct. 23 Test #2 Oct. 25 5.1 – 5.3
6 Oct. 30 5.4 , 5.5 Nov. 1 5.6 , 5.7
7 Nov. 6 Test #3 Nov. 8 6.1 – 6.3, 7.1
8 Nov. 13 7.2 – 7.5 Nov. 15 8.1, 8.2, 8.3
9 Nov. 20 8.4 – 8.7 Nov. 22 Gobble-Gobble
10 Nov. 27 8.9, 9.1, 9.2 Nov. 29 Test #4
11 Dec. 4 10.1, 10.3, 10.5 Dec. 6 10.6, 10.7
12 Dec. 11 Final Review Dec. 13 Final Exam
Dec. 11 Test #5 (optional)
Course Subjects
Chapter 1: This chapter covers all the whole number operations and related applications and algebraic topics. You should concentrate on the vocabulary, translating, and property concepts. In sections 1.8 and 1.9 concentrate on the algebraic concepts. The applications in chapter one are fairly straightforward and students will be tempted to just write down the answer. Don't. Instead create a systematic process of problem solving.
Chapter 2: Chapter two introduces signed numbers. Signed numbers will be with you throughout your study of mathematics.
Chapter 3: Chapter three introduces some basic algebraic concepts and geometry formulas. This early introduction to basic algebraic concepts allows students to continue to integrate algebra with arithmetic throughout the text.
Chapter 4: The understanding of fractions, ratios, and proportions are concepts covered in the fourth chapter. Sections 4.3 and 4.4 (simplifying fractional expressions) are the most important.
Chapter 5: Chapter 5 covers the arithmetic of fractions. Concentrate on understanding the algorithms of fraction operations. This will help you in later courses when you work with rational expressions.
Chapter 6: Chapter six covers the basic operations of polynomials. Omit 6.4.
Chapter 7: Chapter seven covers solving equations and solving word problems using equations. It is very important for students to learn to solve equations of the form ax + b = c.
Chapter 8: Decimals and percents are covered in chapter eight. You should move quickly through the first half of chapter eight and save some time for the last five sections on percents. We cover all of the material in chapter eight; however, section 8.7 and 8.8 cover the same concept using different methods.
Chapter 9: The syllabus covers only the first two sections of chapter nine on reading different types of graphs and calculating the mean, median, and mode.
 Folder Color is a neat tool to customize your Mac OS X folder icon, create colorful and unique folder icons for your computer to classify and manage your folders highly efficient. Folder Colorizer allows you to customize your folders with just about any color. Would like to make your folders looks cool? Or want to organize your folders to make things easier to find? Change the color of your folders and make them distinguishable! Folder Colorizer is the coolest and easiest way to colorize your folders, with just a few clicks, everything is done for you. You can even colorize folders / restore color in batch.
Folder Color is a neat tool to customize your Mac OS X folder icon, create colorful and unique folder icons for your computer to classify and manage your folders highly efficient. Folder Colorizer allows you to customize your folders with just about any color. Would like to make your folders looks cool? Or want to organize your folders to make things easier to find? Change the color of your folders and make them distinguishable! Folder Colorizer is the coolest and easiest way to colorize your folders, with just a few clicks, everything is done for you. You can even colorize folders / restore color in batch.
Chapter 10: The syllabus covers all of chapter ten, except sections 10.2 and 10.4. This is the only geometry that students will learn, so it is important for them to know how to use the formulas.
Student Learning Outcomes/Learning Objectives
Overall objectives:
1. Students will feel a sense of accomplishment in their increasing ability to use mathematics to solve problems of interest to them or useful in their chosen fields. Students will attain more positive attitudes based on increasing confidence in their abilities to learn mathematics.
2. Students will learn to understand material using standard mathematical terminology and notation when presented either verbally or in writing.
3. Students will improve their skills in describing what they are doing as they solve problems using standard mathematical terminology and notation.
Student Learning Outcomes: Upon successful completion of this course, a student will be able to do:
I.Concepts and skills associated with whole numbers
1.write the standard form of a whole number
2.round whole numbers and use rounding to estimate values involving whole number arithmetic
3.perform the four basic arithmetic operations (+, -, x and ÷) on whole numbers
4.solve application problems involving the four basic operations on whole numbers
5.identify the order relation between two whole numbers
6.simplify exponential expressions with whole number exponents
7.use the order of operations to simplify expressions.
8.prime factor whole numbers
9.find the least common multiple of two or more whole numbers
II.Concepts and skills associated with fractions
1.perform the four basic arithmetic operations on fractions
2.solve application problems involving the four basic operations on fractions
3.simplify fractions to lowest terms
4.convert between mixed numbers and improper fractions
5.use the order of operations to simplify expressions with fractions, exponents, grouping symbols,
6.identify the order relation between two fractions
III.Concepts and skills associated with decimals
1.write the standard form of a decimal

2.round decimals and use rounding to estimate values involving decimal arithmetic
3.perform the four basic arithmetic operations on decimals
4.solve application problems involving the four basic operations on decimals
5.convert between fractions and decimals
6.use the order of operations with decimals, exponents, grouping symbols, arithmetic operations.
7.identify the order relation between two decimals or between a decimal and a fraction
IV.Concepts and skills associated with integers and rational numbers
1.perform the four basic arithmetic operations on rational numbers
2.use the order of operations with rational numbers, exponents, arithmetic operations
3.solve application problems involving the four basic operations on rational numbers
4.identify the order relation between two rational numbers
V.Concepts and skills associated with ratios, proportions and percents
1.convert between fractions and percents and between decimals and percents
2.solve percent equations
3.find the missing number in a proportion
1.2 Operations With Rational Numbersmr. Mac's Page Key
4.solve ratio and proportion application problems
5.solve application problems involving percents
VI.Concepts and skills involving linear equations in one variable
1.solve linear equations in one variable involving integers, decimals and fractions
2.solve application problems that yield linear equations
VII.Concepts and skills associated with polynomials
1.identify terms of a polynomial, and classify polynomials by number of terms
2.use the exponent laws to simplify algebraic expressions involving whole number exponents

3.use the order of operations to evaluate variable expressions and formulas
4.combine like terms
5.add and subtract polynomials
6.multiply monomials by polynomials
VIII.Use statistics to collect and interpret data
1.determine the mean, median, and mode
2.interpret graphs (pictographs, circle graphs, bar graphs and line graphs) and analyze data
IX.Concepts and skills associated with geometry
1. know the appropriate vocabulary/facts about angles, triangles, rectangles, squares, and circles
2. find perimeters of rectilinear figures
3. use standard formulas to find perimeters and areas of triangles, rectangles, squares and circles
1.2 Operations With Rational Numbersmr. Mac's Page Number
4. find complementary and supplementary angles
1.2 Operations With Rational Numbersmr. Mac's Page Numbers
5. find angles associated with parallel lines cut by a transversal